
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Cross-border payments are a crucial aspect of global commerce, enabling individuals, businesses, and organizations to conduct transactions across international borders. However, these transactions are often hindered by high fees and long processing times.
Fortunately, blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changing solution for cross-border money transfers, providing cost-saving, blazing-fast, and most importantly, transparent transactions. Today, there are various blockchain-based payment platforms in existence, and many more to come.
In this blog post, we will explore the shortcomings of the existing cross-border payments system and how blockchain technology offers a more efficient alternative. We will also examine the opportunities and challenges that the future holds for this blockchain application.
How do traditional cross-border payments work?
The traditional payments stack is made up of three to five financial parties that work together. These parties manage the funds and ensure that transactions are executed, but this trust comes at a cost to senders as each party will take a small cut of the transaction.
There are several different methods for making such payments, including debit/credit cards, wire transfers, SWIFT/SEPA, and neo-banks. These methods usually cost you 1 to 3% of the transaction and take up to 3 days to process.
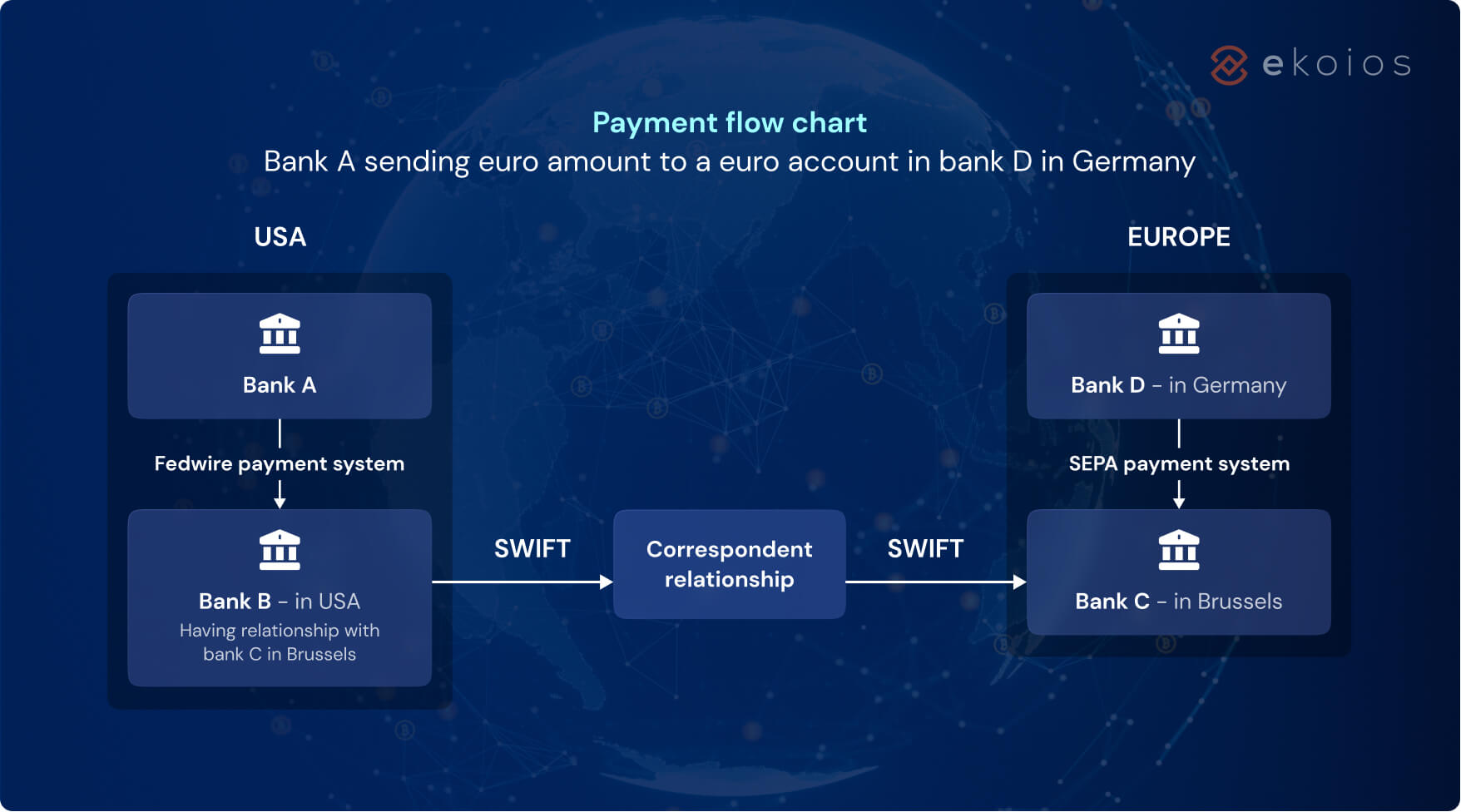
🔎 Take this example of bank A sending a euro (EUR) amount to a EUR account in bank D using SWIFT. The procedure goes as follows:
- A payment message in $US (in SWIFT format) is sent to bank A in the US.
- Bank A sends the payment request to its correspondent bank, bank B via Fedwire and includes a debit/credit instruction for onward transmission.
- Bank B performs the necessary adjustments and sends a message to its correspondent bank, bank C in Brussels via the SWIFT network.
- Bank C transmits the value via the Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) to bank D in Germany.
- Bank D credits the supplier account in EUR.
The problem with traditional payment systems
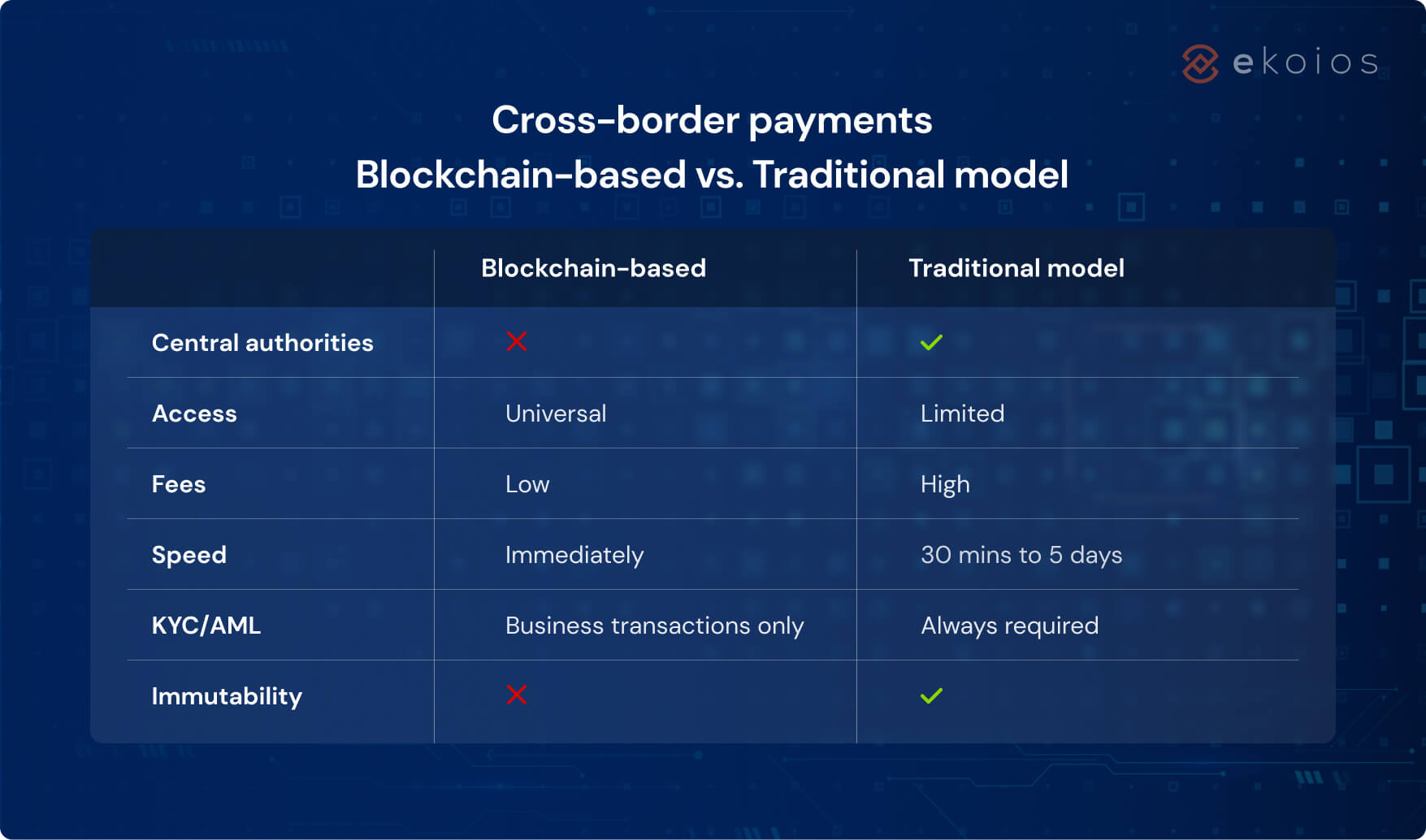
- Centralized control: Traditional payment systems involve central authorities such as banks and the government. These entities have full control of all information and can share it without warning. However, misuse of this power could create long-term trust issues – just take a look at the recent downfall of Sillicon Valley and Signature Banks.
- Lack of universal access: With lower economically developed regions, access to financial services is severely limited, making cross-transfer payment impossible. In the majority of African countries, not even half the people have a bank account to perform such transactions (source: The Global Economy)
- High transaction fees: Banks and other financial institutions often charge hefty fees for international payments – some even taking up to 5% of the transaction! Thus, for small businesses or individuals, it can be hard to justify making cross-border payments as the fees outweigh the benefits.
- Time-consuming procedure: Depending on the chosen method, an international transfer may take from 30 minutes to 5 days. Moreover, the transfer will require detailed information about both the sender and receiver, plus a lengthy identity verification process.
- Security vulnerabilities: With so many parties involved in the process, there are many opportunities for fraud or cyber-attacks. In addition, different countries have varying levels of regulatory oversight and consumer protection laws, making it difficult to ensure that all transactions are secure and protected.
Blockchain application in cross-border payment
But first, what is blockchain? It’s a secure, transparent, and immutable way of storing and transferring information via a distributed digital ledger. Blockchain uses a network of computers to store and update the ledger without any central server. Each computer in the network has a copy of the ledger, and each transaction is recorded and verified by the network.
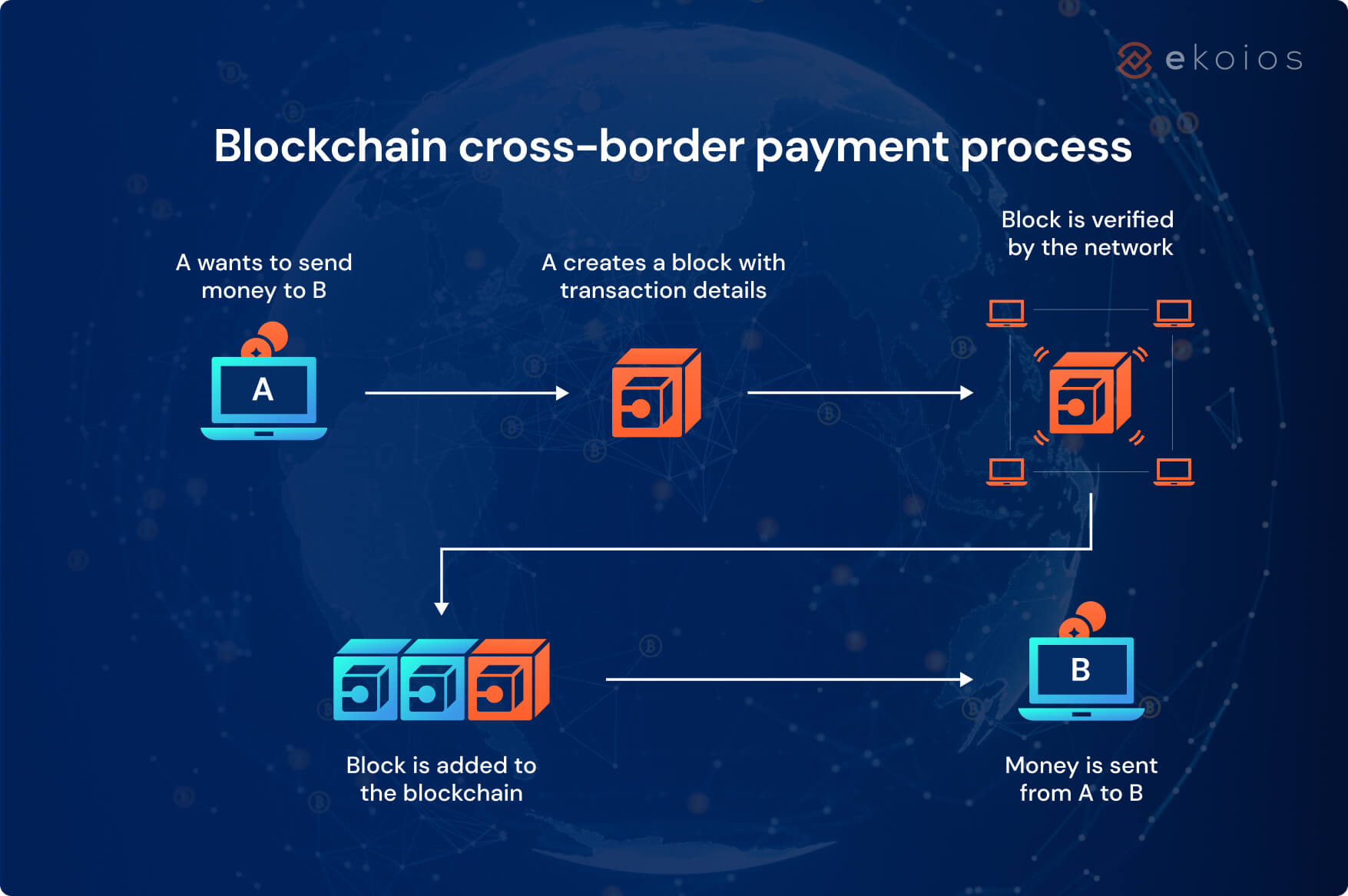
Applying blockchain technology to cross-border payment, we can solve all of the problems mentioned above:
- Decentralization: Unlike traditional payment systems, there is no need for intermediaries to facilitate transactions. This means that individuals or businesses can directly conduct the transfer by themselves. ( Read more about Defi)
- Universal Access: Blockchain networks are global and accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This makes it easy for people to send and receive payments from anywhere in the world, regardless of their location or currency.
- Low Fees: Instead of transaction fees, blockchain has gas fees as a way to compensate the network nodes for the computational power needed to process and validate transactions. Be noted that gas fees can vary depending on network congestion and other factors, so during times of high demand, gas fees can be quite high. However, there are many ways to optimize this cost, and developers are working on innovative solutions to address this issue.
- Effortless Procedure: This should be a no-brainer – blockchain transactions are completed within seconds, and all it requires is a wallet address to transfer the fund to.
- Immutability: Blockchain ensures that once a transaction has been recorded on the ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted. This adds an extra layer of security and trust to the payment process, as it prevents fraudulent activity and ensures that all transactions are accurate.
🔸 Read about 6+ more blockchain use cases beside cross-border payments
Opportunities and Challenges
Cross-border payments are considered one of the most potential markets for blockchain, thanks to its outstanding advantages over traditional methods. In 2021, it represented 15.9% of the $4.67 billion global blockchain market, according to the IDC Worldwide Blockchain Spending Guide.
The industry is anticipated to grow in tandem with the anticipated growth of the global blockchain market, which is boldly predicted to expand from just $7.18 billion in 2022 to $163.83 billion by 2029. Juniper Research also estimates that, by 2024, B2B cross-border payments on blockchain will make up 11% of the total B2B international payments.
Various platforms and solutions have since emerged, providing fast, secure, and transparent blockchain-based cross-border payments. A few notable names include:
- Ripple: both an open source protocol for payments, as well as a digital currency called Ripple (XRP).
- Liink (Pre. Interbank Information Network) by JPMorgan: the global finance firm’s first scalable, peer-to-peer network powered by blockchain technology.
- Electroneum: provides an easy and fast way to get paid, and top up essential services with ETN currency.
- Celo: the mobile-first blockchain optimized for peer-to-peer payments using only a mobile number.
- Stellar: an open-source distributed payments infrastructure, aimed to streamline international money transfers.
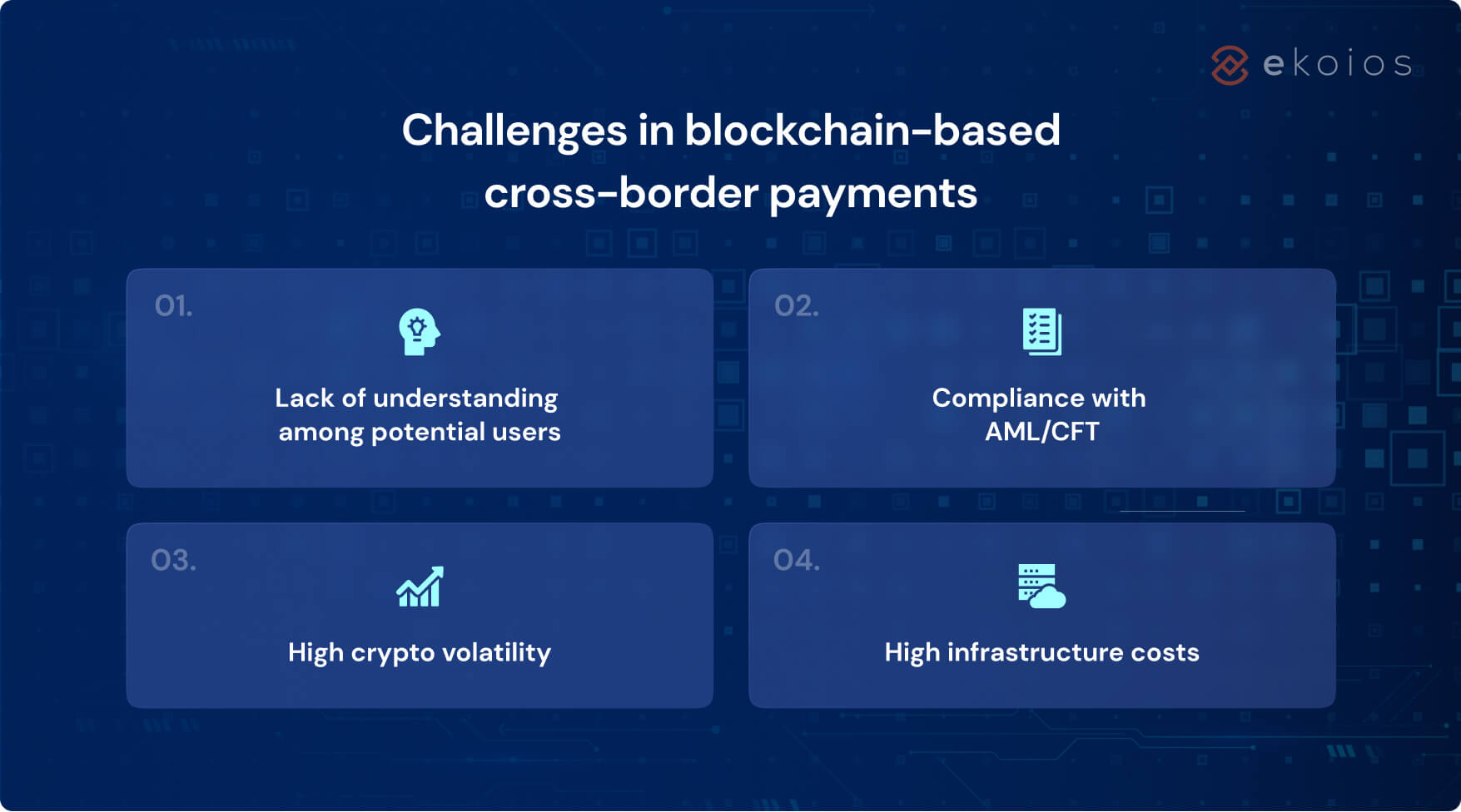
However, major challenges still remain for the technology to be widely accepted. Blockchain knowledge is not widely common and the overall user experience is rather cumbersome, which can create a barrier to adoption. Compliance with AML/CFT regulations is also crucial for ensuring that blockchain-based payments are secure and transparent. However, this can be challenging because these regulations often require extensive KYC (Know Your Customer) and CDD (Customer Due Diligence) procedures that contrast blockchain’s anonymous nature.
Furthermore, the high volatility of the cryptocurrency market can make it difficult for businesses to accurately calculate the fiat-to-crypto amount before the transaction actually takes place, or store crypto in the wallet for long-term use. Last but not least, implementing a blockchain-based payment system requires significant infrastructure investment in terms of hardware and software development.
Conclusion
Cross-border payments, which used to be a costly, centralized, and lengthy process, have been revolutionized by the application of blockchain. The only question left now is getting it ready for mass adoption.
If international transfer is considered an integral part of your business – then it’s time to catch up with the revolution. Ekotek’ team of world-class blockchain analysts and developers have years of experience building solutions for financial institutions, from a small wallet or token distribution portal to full-blown marketplaces, crypto exchanges, and private blockchain platforms. Contact us today to explore the full blockchain potential, and get a tailored solution to your business needs!
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5